Data Structure 1 - Queue/Stack/Hash
1. Min Stack
The stack should support push, pop and min operation all in O(1) cost
class MinStack {
public:
MinStack() {}
// 用单调栈,省一些空间,但时间复杂度不变,而且pop多了判读会慢
void push(int number) {
data.push(number);
// 是否更新最小值, 注意等于号!
if (mins.empty() || number <= mins.top()) mins.push(number);
}
int pop() {
int cur = data.top();
if (cur == mins.top()) {
mins.pop();
}
data.pop();
return cur;
}
// mins和data同增同减
void push(int number) {
if(mins.empty() || number < mins.top()) {
mins.push(number);
} else {
mins.push(mins.top());
}
data.push(number);
}
int pop() {
int res = data.top();
data.pop();
mins.pop();
return res;
}
int min() { return mins.top(); }
private:
stack<int> data;
stack<int> mins; // 记录最小值变化序列
};2. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3], return 10
为何不能使用DP:是求最大;是必须有序序列;但不是暴力复杂度
此题暴力解法为O(n^2), DP不适合优化此类算法(适合2^n->n^2)
nlogn: merge sort, quick sort(两半,O(n)时间合起来); 先sort; for…内部数据结构logn的操作,Tree Style
n: 单调栈 [1,4,5] -> push(2) -> [1,2]
一个pop操作的时候,可以知道某个数左边第一个比它小的数;右边,第一个比它小的数
解法:木桶原理,求每个柱子往左往右最大延伸的矩形(左右第一个比它小的数)
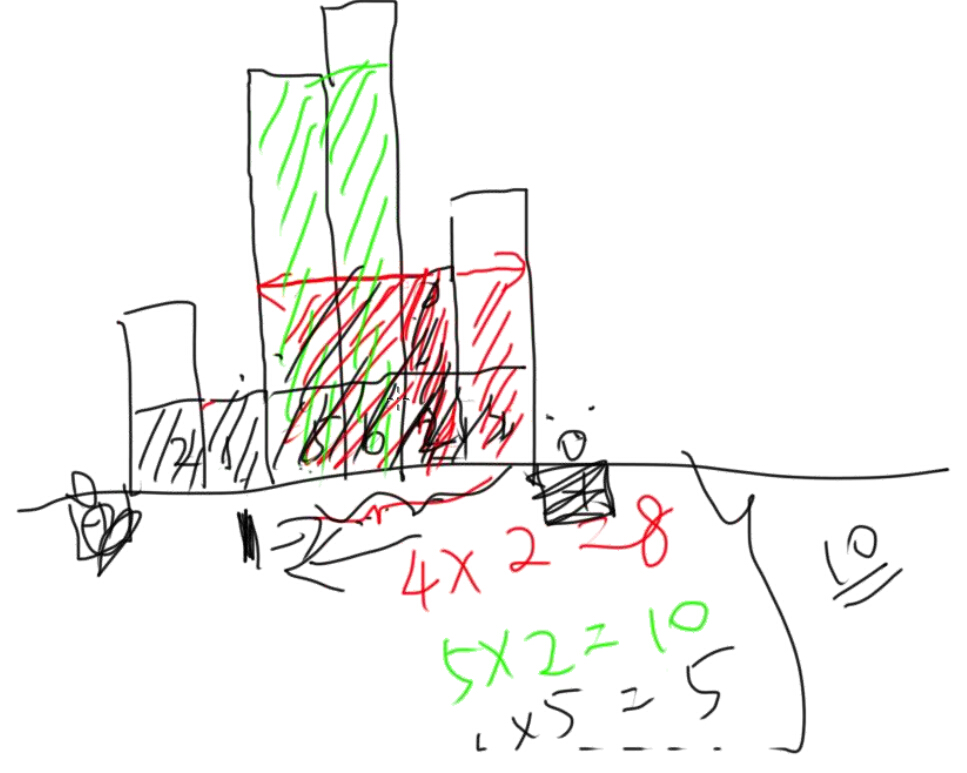
// O(n) time and memory, 每个数在stack上都进出一次;同理,binary tree相关,每个节点O(1),共n个点,所以O(n)
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) {
int res = 0; // 初始值为0,最小或为空都是0
stack<int> incStack; // 因为求距离,所以加的是下标
for (int i = 0; i <= height.size(); i++) {
int cur = i == height.size() ? 0 : height[i]; // 最后填0把所有的弹出来
while (!incStack.empty() && cur <= height[incStack.top()]) { // cur <= 也可以!
int h = incStack.top();
incStack.pop();
int w = incStack.empty() ? i : i - incStack.top() - 1; // 空的时候为i,不空记得-1(代数进去算需要-1)
res = max(res, height[h] * w); // 找的是弹出去的这个index的高度,以它为最矮的最大的面积
}
incStack.push(i);
}
return res;
}
// 暴力解法,O(n2) 超时
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &heights) {
// 暴力 O(n2)
int area = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {
int minh = heights[i];
for(int j = i; j < heights.size(); j++) {
minh = min(minh, heights[j]);
area = max(area, (j - i + 1) * minh);
}
}
return area;
}3. Maximal Rectangle
Given a 2D boolean matrix filled with False and True, find the largest rectangle containing all True and return its area.
Given a matrix:
[
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
]
return 6.
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<bool> > &matrix) {
// O(n^4) 暴力解法, TLE超时
int res = 0;
if (matrix.size() == 0) return res;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++) {
// 枚举每个左上角,之后枚举右下角
if (matrix[i][j] == 0) continue;
int maxy = matrix[0].size() - 1; // 右边最远的位置
for (int k = i; k < matrix.size(); k++) {
for (int z = j; z <= maxy; z++) {
if (matrix[k][z] == 0) {
maxy = z - 1;
break;
}
res = max(res, (k - i + 1) * (z - j + 1));
}
}
}
}
return res;
}单调栈解法O(n^2)
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<bool> > &matrix) {
int rows = matrix.size();
if (rows == 0) return 0;
int cols = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> height(cols, 0);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 1) {
height[j]++;
} else {
height[j] = 0;
}
}
res = max(res, largestRectangleArea(height)); // 上题函数
}
return res;
}4. Max Tree
Given an integer array with no duplicates. A max tree building on this array is defined as follow:
The root is the maximum number in the array
The left subtree and right subtree are the max trees of the subarray divided by the root number.
Construct the max tree by the given array.
Given [2, 5, 6, 0, 3, 1], the max tree constructed by this array is:
6,5,3,2,#,0,1
// O(n) time and memory, Hard
TreeNode *maxTree(vector<int> A) {
if (A.size() == 0) return NULL;
stack<TreeNode *> incS;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) {
TreeNode *cur = new TreeNode(A[i]);
while (!incS.empty() && A[i] > incS.top()->val) {
cur->left = incS.top(); // 一直更新left
incS.pop();
}
if (!incS.empty()) incS.top()->right = cur; // 一直更新right
incS.push(cur);
}
while (incS.size() > 1) incS.pop();
return incS.top();
}5. Implement Stack by Two Queues
The queue is first in first out (FIFO). That means you can not directly pop the last element in a queue.
class Stack {
public:
// Push a new item into the stack
void push(int x) {
if (q1.empty())
q2.push(x);
else
q1.push(x);
}
// Pop the top of the stack
void pop() {
if (q1.empty()) {
while (q2.size() > 1) {
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
q2.pop();
} else {
while (q1.size() > 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
q1.pop();
}
}
// Return the top of the stack
int top() {
int res;
if (q1.empty()) {
while (q2.size() > 1) {
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
res = q2.front();
q2.pop();
q1.push(res);
} else {
while (q1.size() > 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
res = q1.front();
q1.pop();
q2.push(res);
}
return res;
}
// Check the stack is empty or not.
bool isEmpty() { return q1.empty() && q2.empty(); }
private:
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
};上述方法,pop和top代码复杂,且top的时间复杂度高O(n),改进push时候倒腾为O(n),pop和top是O(1):
class Stack {
public:
// Push a new item into the stack
void push(int x) {
if (q1.empty()) {
q1.push(x);
while (!q2.empty()) {
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
} else {
q2.push(x);
while (!q1.empty()) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
}
}
// Pop the top of the stack
void pop() {
if (q1.empty()) {
q2.pop();
} else {
q1.pop();
}
}
// Return the top of the stack
int top() {
if (q1.empty()) {
return q2.front();
} else {
return q1.front();
}
}
// Check the stack is empty or not.
bool isEmpty() { return q1.empty() && q2.empty(); }
private:
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
};6. Implement Queue by Two Stacks
Implement it by two stacks, do not use any other data structure and push, pop and top should be O(1) by AVERAGE.
class Queue {
public:
stack<int> stack1;
stack<int> stack2;
Queue() {}
void push(int element) { stack1.push(element); }
//!!提取出代码公共部分,简洁
void adjust() {
if (stack2.empty()) { // 好办法,s2中顺序就是实际顺序,空了再往里放,平均复杂度O(1),每个元素出入s1,s2一次
while (!stack1.empty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.top());
stack1.pop();
}
}
}
int pop() {
adjust();
int res = stack2.top();
stack2.pop();
return res;
}
int top() {
adjust();
return stack2.top();
}
};7. [Hash - 由key映射到固定且无规律的位置]
O(1) Insert / O(1) Find / O(1) Delete, 对于string来说,是O(len(str))
Hash Table:线程安全
Hash Map:线程不安全
Hash Set:单元素
Closed Hashing:3种状态占据/空的/deleted
Open Hashing:拉链法,链表
// hash函数示例
// hashcode("abcd") = (ascii(a) * 33^3 + ascii(b) * 33^2 + ascii(c) *33 + ascii(d)) % HASH_SIZE
int hashCode(string key, int HASH_SIZE) {
long long res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < key.size(); i++) {
res = (res * 33 + key[i]) % HASH_SIZE; // %满足+-*交换结合律
}
return res;
}8. Rehashing
If the total size of keys is too large (e.g. size >= capacity / 10), we should double the size of the hash table and rehash every keys
/**
* @param hashTable: A list of The first node of linked list
* @return: A list of The first node of linked list which have twice size
*/
vector<ListNode*> rehashing(vector<ListNode*> hashTable) {
int cap = hashTable.size() * 2;
vector<ListNode*> res(cap, NULL);
for(auto node: hashTable) {
ListNode *curhead = node;
// 遍历该节点
while(curhead != NULL) {
// 先搞一个要插入的点
ListNode *insernode = curhead;
curhead = curhead->next;
insernode->next = NULL; // 封口
// 开始append insernode
int key = (insernode->val % cap + cap) % cap;
// 放到list最后,很奇怪,放到开头更效率高
ListNode *dsthead = res[key];
if(dsthead == NULL) {
res[key] = insernode;
continue;
}
while(dsthead != NULL && dsthead->next != NULL) {
dsthead = dsthead->next;
}
dsthead->next = insernode;
}
}
return res;
}